Videography and editing | PHOTO | VIDEO | MEDIA |...
Read More

Marketing Agency offers a wide range of services that will help your business flourish.
Projects that we have worked on. Name that we have earned. Hearts we have touched.
View our gallery of amazing videos and photographs we have taken for our clients.
We like to help the community by sharing our expertise. Articles that will help you with your business in various ways.

An advertising and marketing professional who has made a name for himself in the creative industry.
Gibran Mallick
Director / Photographer

It’s no longer feasible to run a business, even a brick-and-mortar one, without a web presence. Consumers turn to the internet for everything from product research to location and operating hours. Having even a simple website that’s well-designed can give you an edge in your field, and if you have products to sell, your site can open up new markets and expand your business cheaply and easily.
Website design software has evolved so it’s easier to use now more than ever. You don’t need to know coding to develop an attractive and functional site. No matter what program you use, there are basic rules and tips that will give your website a professional look, make it easy to find, and show your company in the best light.
Here’s our step-by step guide to creating a successful business website.
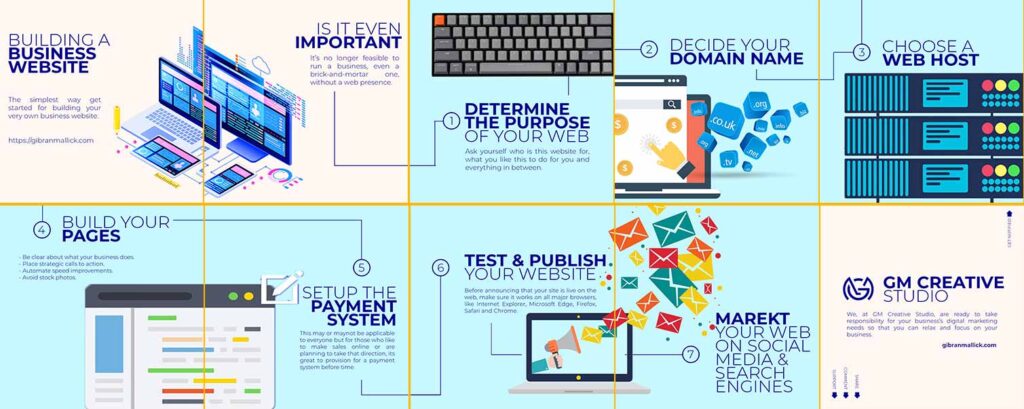
Your domain name is one of the most important features of your website. It’s the URL you’ll be sharing with your current and potential clients and promoting on social media. Therefore, you want it to be descriptive and easy to remember and type in. Try to keep it short, and steer clear of abbreviations, acronyms and numbers if possible, to avoid customer confusion.
Once you’ve selected your domain name, you’ll need to confirm its availability and purchase it through a domain registrar like GoDaddy, Squarespace, Wix or Web.com. Don’t forget to check copyrights to make sure you’re not infringing on anyone else’s protected name with your website. If your preferred URL is already taken, you can call the company and ask to buy it from them.
A business website generally serves as a space to provide general information about your company or a direct platform for e-commerce. Regardless of whether you create a simple website that tells a little about your company or a more complex e-commerce site, the most important thing you must do is say, on the home page in plain terms, what your company does. Do not make customers root around to discover if your company can do what they need.
“Think about your specific user experience, and the journey the user will go through as they navigate your site,” “Whatever the fundamental goal of your website is or whatever the focus may be, users should be easily able to achieve it, and the goal itself should be reinforced as users navigate throughout your site.”
If you don’t plan to accept payments through your website, you won’t have as much work to do in setting it up. If you are a retailer or service provider and want to offer customers the option to pay online, you’ll need to use an external service to receive your payments, which will be discussed later in this article.
Every website needs a “host,” a server where all of the data is stored for the public to access at all times. As a small business, hosting your own website is simply too large an expense, so you’ll need to select an external host.
Depending on your budget, you can follow two different routes. A shared web host, the least-expensive option, means you’ll share a server with other sites. Dedicated hosting costs significantly more, but it means that you get your own private server and won’t have to compete with other sites that could drag down your speed. It’s good to ask, ‘Can you show me how close you are to the major markets my customers are going to be in?'” said CEO GM Creative Studio “Any good hosting provider should have the tools to show you … measurements of their performance,”
A good website is more than a static home page. You’ll want to create multiple pages dedicated to different aspects of your business, such as a detailed catalog of your products or services, or a blog section for company updates. As for your overall website, you want to be sure each page supports the primary goal of the website, has a clear purpose and includes a call to action (e.g., learn more, sign up, contact us or buy this).
A contact page, your customers’ direct link to you, is one of the most important sections of a website, so make sure you include as much information as you can (phone number, email address and physical location, if applicable). It’s also a good idea to include information about the founding team or staff on an “About” page to help customers put real names and faces to your brand.
If your business doesn’t already have a logo, hire a graphic designer or create a logo yourself to use on your website, business cards and social media profiles. This will help your clients identify your company quickly and easily on the web.
Distill what your business does into a clear, concise statement and lead with that. Visitors should be able to understand what you do within seconds of landing on your home page. A few well-written pages are more effective than dozens of poorly written ones.
Call-to-action buttons tend to perform best when they match the information on the page. For example, a “Buy Now” button makes sense on a product page, but not on the About page. Rather a “Contact us to learn more” might be more appropriate. Likewise, a page listing customer reviews might have a button that takes the reader to the available plans and pricing.
Set up as many automated speed improvements as you can. If you use a content management system (CMS), installing the right plugins will cache parts of your site so visitors don’t need to download anything more than once. For WordPress users, it is recommended to use WP Super Cache or W3 Total Cache, which compresses files and allows visitors to browse your site more quickly. Some of the more technical aspects of caching and compressing files may require a Web development partner if you’re not particularly tech savvy.
Cheesy stock photography is the quickest way to turn a great site into a mediocre one. If you’re looking for photos to use on your page, it’s best to use a picture of your actual team or office.
While this step won’t apply to all business websites, companies that want to offer the option to pay online will need to integrate electronic payment systems into their websites. The easiest way to do this is through e-commerce software or third-party payment processors.
Many web hosts offer an in-house shopping cart or integration with e-commerce programs. Do some research to make sure you get a solution that’s easy to work with and flexible enough to meet your needs now and in the future. To explore your e-commerce software options,
Before announcing that your site is live on the web, make sure it works on all major browsers, like Internet Explorer, Microsoft Edge, Firefox, Safari and Chrome. Click through each page and feature on every browser to ensure images show up, links are correct and the format looks smooth. This will take some time, but the effort you put in now will save future complaints from visitors who can’t access certain features.
Another important feature to incorporate into your website from the very beginning is an analytics program. By setting this up before the website is live, you can iron out any issues and coordinate a proper setup, Shaoolian said. Once the website is live, you can monitor page performance and determine why a page is successful or unsuccessful based on your analytics.
Social media, whether Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn or Pinterest, is the best way to increase your audience reach and alert customers and clients about what’s going on with your company. Whenever you update your website, post about it on your social media outlets — but balance that out with genuine, nonpromotional engagement.
Submitting your website to major search engines will also help direct potential leads to your page, as will deploying a strong search engine optimization (SEO) strategy across your site. It is said that defining title tags, meta-descriptions and uniform resource identifiers (URIs) that are relevant to your company and aspects of your industry will help ensure that you rank correctly in search engines for the products or services that you’re trying to market.
Staying relevant is important, so update your website frequently with blog posts on current industry events, new products and offers, and company news to keep visitors coming back to the site.
You should also check at least monthly to ensure your software and all add-ons are up to date. Pheil said that if your software is not up to date, it’s in danger of being hacked, even if the website host’s security is strong. If you don’t have time to do this yourself, delegate the task to a trusted employee or hire a freelance website manager.
Starting a website for your business is a low-cost investment that will help you to both establish credibility and reach a wider customer base than you ever could through traditional marketing techniques. If you keep your website updated with fresh, current content and are quick to address technical issues, you’ll never have to worry about “not existing” to your current and future clients.
Corporate headshot | portrait photography | PHOTO | VIDEO |...
Read MoreNo matter where you are or who you are; we are here for you when ever you need us. Drop us a line today and we will get in touch with you as quickly as possible because we at GM Creative Studio believe you are important to us.